Are you experiencing persistent bad breath, swollen gums, or bleeding while brushing? These seemingly innocuous signs might actually be indicators of a significant oral health concern – gum disease. Also known as periodontal disease, gum disease is a condition that affects the tissues supporting the teeth and can lead to severe consequences if left untreated. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of gum disease detection, its implications, and the crucial role of early identification.
Understanding Gum Disease
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the gum tissues surrounding teeth. It begins with the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, on the teeth. If not adequately removed through regular brushing and flossing, plaque can turn into tartar, leading to inflammation and potential damage to the gums and bone supporting the teeth.
Causes of Gum Disease
The primary cause of gum disease is poor oral hygiene. Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to build up, leading to the release of toxins that irritate the gums. Other factors, such as smoking, genetics, hormonal changes, and certain medical conditions, can also contribute to the development of gum disease.
The Stages Of Gum Disease
Gingivitis: The Early Stage
Gingivitis is the initial stage of gum disease. It is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. Fortunately, gingivitis is reversible with proper oral care and professional dental cleanings.
Periodontitis: Advanced Gum Disease
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis. In this stage, the inner layer of the gum and bone pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that can become infected. Without intervention, periodontitis can lead to tooth mobility and even tooth loss.
Signs And Symptoms
Common Indicators
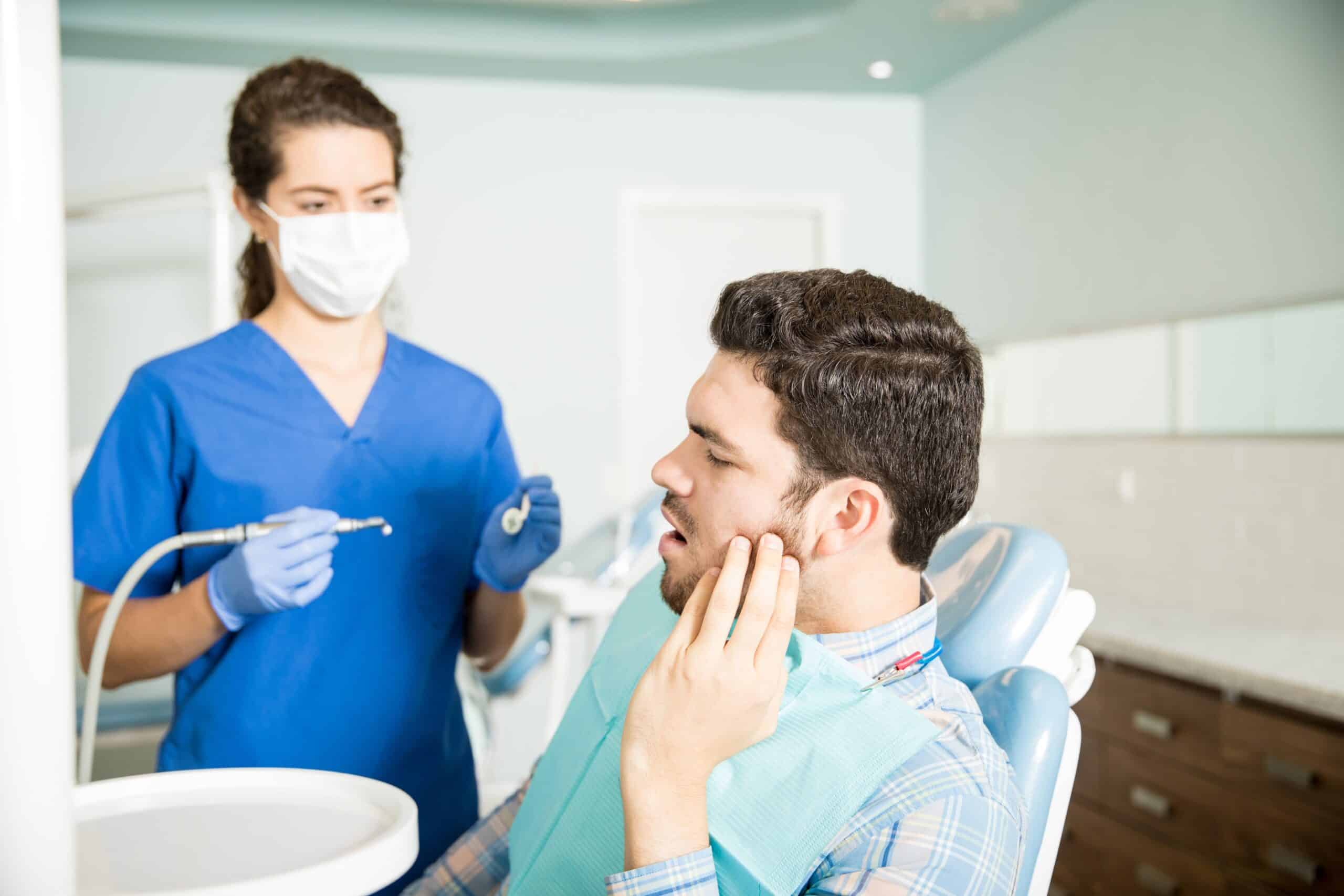
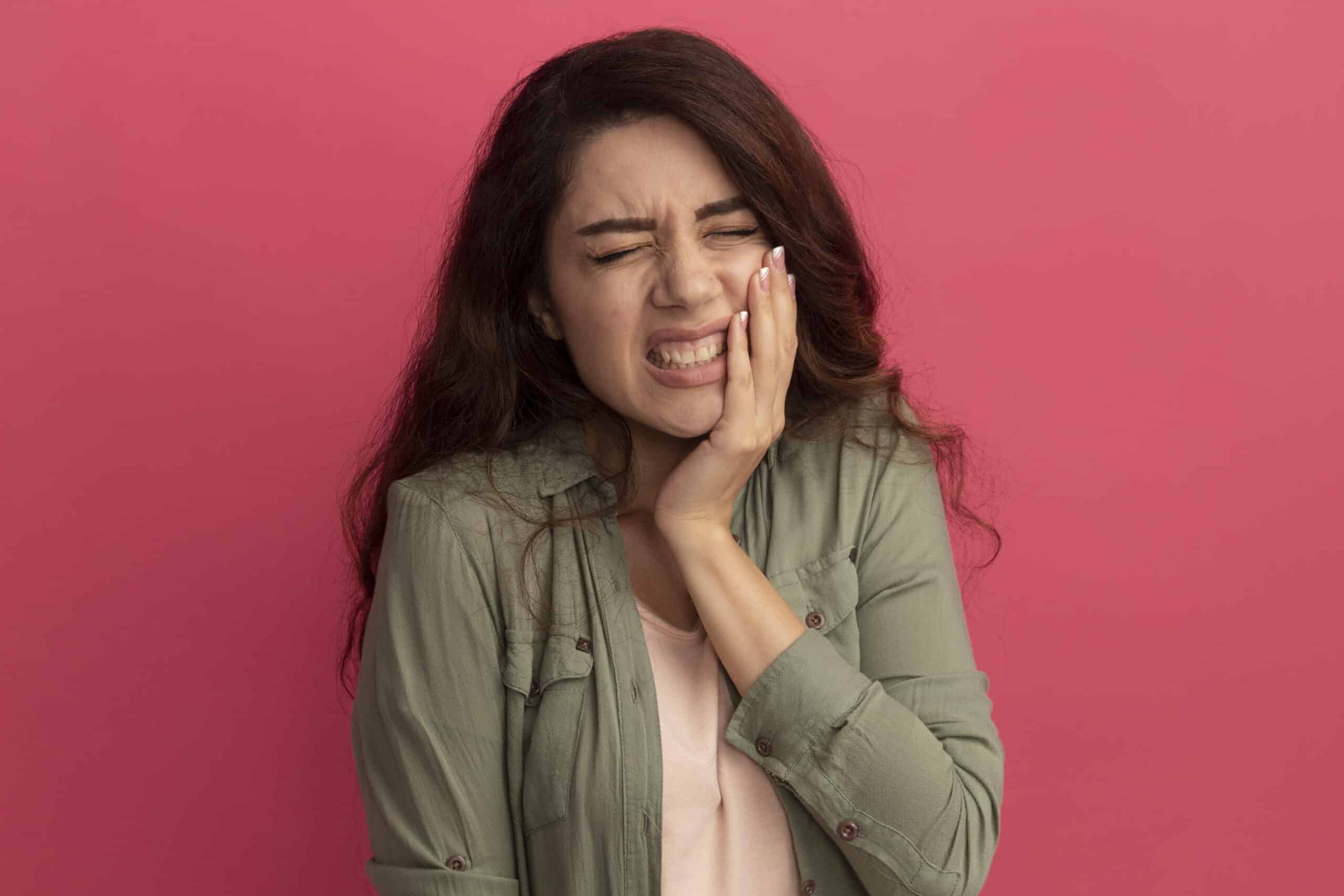
Early signs of gum disease include persistent bad breath, gum redness and swelling, bleeding while brushing or flossing, and sensitive teeth. As the disease advances, you might experience receding gums, pus between the teeth and gums, and changes in your bite.
The Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are essential for detecting gum disease in its early stages. Dentists can identify subtle signs of inflammation and provide guidance on maintaining optimal oral health.
Diagnosis Techniques
Visual Examination
Dentists visually inspect the gums for signs of inflammation, recession, and pockets. This initial assessment helps determine the presence and severity of gum disease.
Dental Probing
Using a tiny ruler-like instrument, dentists measure the depth of the pockets around each tooth. Deeper pockets can indicate advanced gum disease.
X-rays and Imaging
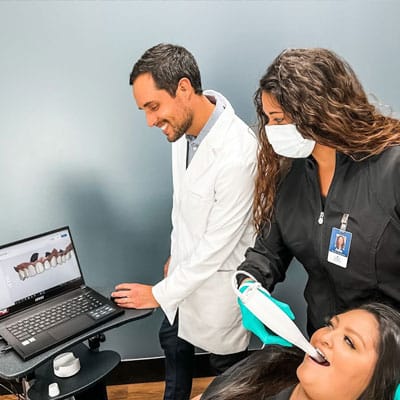
X-rays reveal the extent of bone loss and help dentists determine the best treatment approach. Advanced imaging techniques like digital scans provide detailed 3D images of the oral structures.
Importance of Early Detection
Preventing Progression
Early detection of gum disease allows for timely intervention, preventing its progression to more severe stages. Proper management can help save your teeth and preserve your smile.
Preserving Oral Health
Gum disease has been linked to various systemic health issues, including heart disease and diabetes. Detecting and managing gum disease can contribute to overall well-being.
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Approaches
Non-surgical treatments include scaling and root planing, which involve deep cleaning to remove tartar and bacteria from the pockets.
Surgical Interventions
Advanced cases may require surgical procedures like flap surgery or bone grafts to restore gum health and prevent further damage.
Technological Advancements
Laser Dentistry
Laser therapy is used to remove inflamed gum tissue and promote healing. It is minimally invasive and reduces discomfort.
Digital Imaging
Advanced imaging techniques provide precise assessments of gum disease, aiding in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Gum disease is a prevalent oral health concern that can have serious implications if left untreated. Early detection through regular dental visits, proper oral hygiene, and a healthy lifestyle plays a pivotal role in preventing its progression. By taking proactive steps to care for your gums, you can ensure a healthy smile that lasts a lifetime.